Women make up the majority of our population, but they encounter various problems and disadvantages due to their gender and biases. They constantly endure manipulation and violence in a male-dominated society.
Since ancient times, people in India have subjected women to abuse at many levels—social, economic, physical, psychological, and sexual.
Before the implementation of the Constitution, no one knew about the concept of gender equality. Then in the 20th century, women started to claim their rights. Having economic independence will improve women’s lives and elevate their status.
Women’s rights, especially in the workplace, are more complicated than ever before. ‘Right to Work’ includes protection against sexual harassment at work.
To protect against sexual harassment at work, Indian legislation implements the Prevention of sexual harassment at Work Place (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act, 2013(POSH ACT). As a result, with the help of POSH training women are safe in the workplace from sexual harassment.
Meaning of sexual harassment
Sexual harassment is any disagreeable comment, action, gesture, or any action that is sexual in nature like sexual advantage, request for sexual favors, and verbal or physical harassment in the workplace or learning environment, according to the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC).
It does not always have to be particularly about sexual behavior or directly for a particular person. For example, negative comments about women from a group are also sexual harassment.
Sexual harassment includes many things:
- Attempted or actual rape or sexual harassment
- Force for doing sexual behavior.
- Unwanted Touching, leaning over, or pinching.
- Unwelcome sexual looks or gestures
- Unpleasant letters, phone calls, and materials sexual in nature.
- Unwanted pressure for dates.
- Calling from other names like girl, doll, baby, honey, etc.
- Whistling at someone.
- Cat calls.
- Sexual comments.
Sexual harassment can be verbal, non-verbal, and physical. Here are some examples:
Verbal:
Telling sexual jokes or stories, making sexual comments about a person’s body, Wrong comments on someone’s clothing, making kissing sounds, howling, smacking lips, repeatedly asking a person out who is not interested, telling lies or spreading rumors about a person or her personal life and etc.
Non-verbal:
Looking at a person with elevator eyes (up and down), Continuing staring at a person, blocking a person’s path, Following them, giving someone personal gifts, making sexual gestures with hands or through body movement, winking, throwing kisses or licking lip in the wrong way.
Physical:
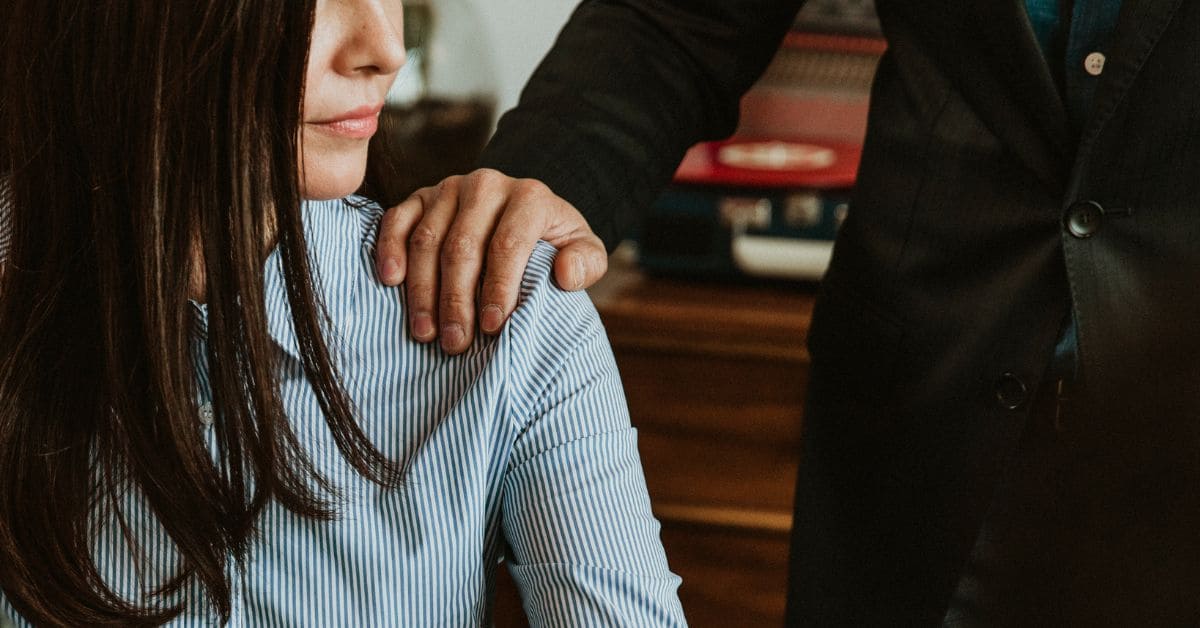
Giving a massage around the neck or shoulder, touching the person’s clothes, hair, or body, hugging, kissing, patting or stroking, touching or rubbing someone sexually around other people, standing close or brushing up against another person.
What is Sexual harassment we tell in detail how To prevent women from that Indian legislation introduced POSH Act.
POSH Act
Prevention of sexual harassment at Work Place (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act, 2013(POSH ACT) mandates that every organization should provide a safe and secure working environment free from sexual harassment for women.
Institutions were introduced to three key obligations to meet that standard, namely:
- Prevention
- Prohibition
- Redressal
It is important to know that the Act provides a civil remedy to women and is in addition to other laws which are currently in force.
Accordingly, any woman who wishes to report an instance of sexual harassment at work has the right to take action and recourse for both civil and criminal proceedings.
So there are certain rules for both government and private organizations with 10 or more employees mandated by the law to comply with specific requirements to form an internal complaints committee (ICC).
Any female employee in their organization should manage ICC and file a formal sexual harassment complaint, as well as conduct POSH training.
The ICC has the power to investigate sexual harassment complaints and redress them in the manner identified under the POSH Act and POSH Rules.
If a company has different branches at different locations then they have to constitute ICC in each such administrative division. Skills ally is one of the best organization who provides POSH training.
For organizations with fewer than ten employees, it is not mandatory to constitute the ICC and complaints pertaining to sexual harassment in this case if someone faces a problem they can go to the local complaints committee which is set up by district officers according to the POSH Act.
History of the POSH Act
The beginning of POSH legislation started with Bhanwari Devi’s fight for justice, which continues to this day.
It paved the way for the historic case of Vishakha. The “Vishaka Guidelines” governed employer responsibilities in addressing workplace sexual harassment until the POSH Act was passed, with Rajasthan leading the way. Before the POSH Act, organizations followed the Vishaka Guidelines.
Bhanwari Devi was a social worker from Bhater (Rajasthan) who was gang raped in 1992 by 5 men angered by her efforts to prevent child marriage in their family. She began the thought of women’s safety in the workplace and now we can see POSH.
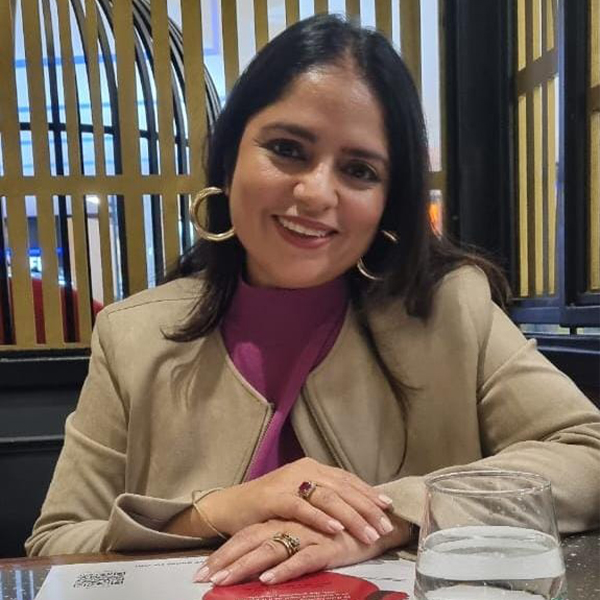

Ramanjeet Kaur is a Life Skills and Behavioural Trainer. Her journey to becoming an entrepreneur and starting her career as a trainer in the education industry is an inspiring revelation. She was always passionate about teaching profession from her childhood and started mentoring young kids to develop their personalities.